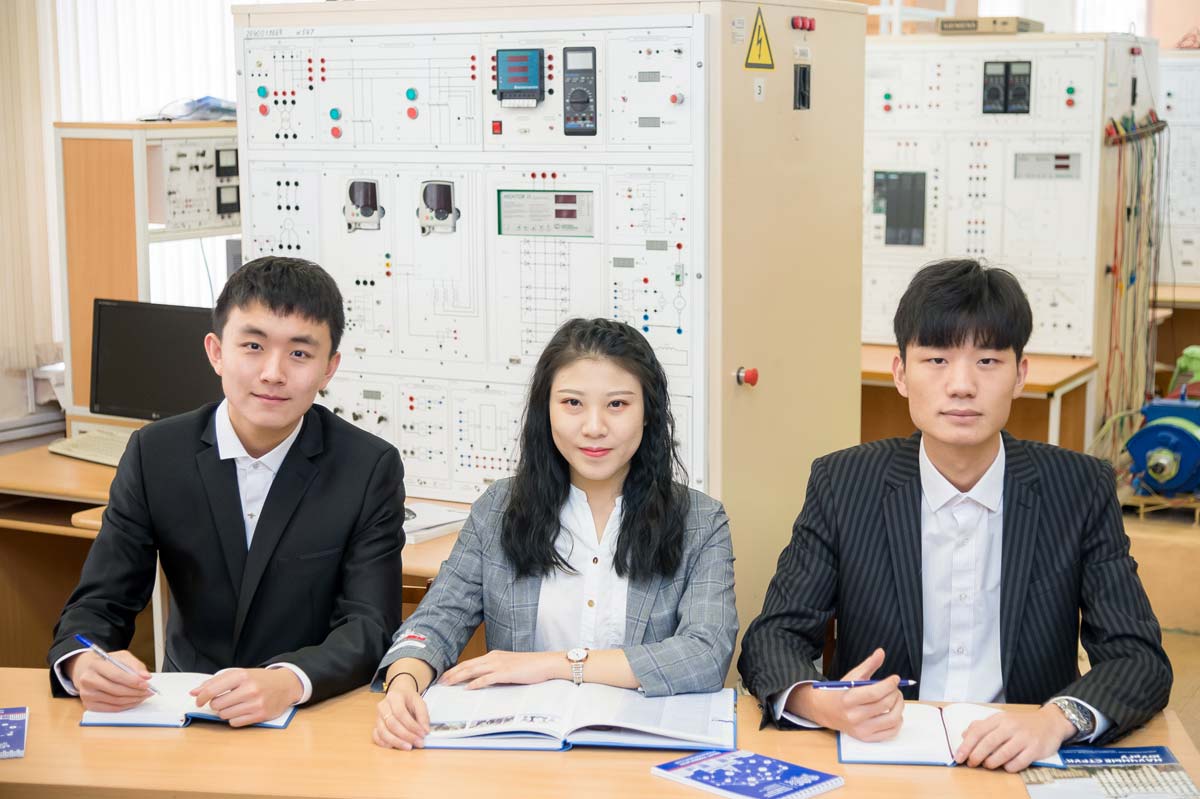
The goal of teaching is to prepare students to go into industry. The excellence in teaching comes naturally from the excellence in research. In the epoch of digitalization and IoT the key words to describe our approach to teaching are INTERDISCIPLINARITY, HANDS-ON EXPERIENCE and PROJECT LEARNING.
- Software engineering is often a major part of electrical power engineering or heat power engineering.
- SUSU Power engineering programs are designed to seamlessly combine theory and practice and to provide hands-on, reality-based learning experiences, tailored to our students’ professional needs.
TEACHING METHODS:
- Electronic data processing and analysis (including big data analysis) – will allow you to make sense of the collected data
- Modeling and Simulations needed to successfully apply models and algorithms to solve real-life energy problems;
- Testing, operating and maintenance
Our students learn how to:
- operate and maintain pump stations, electrical generators, systems of refrigeration and air-conditioning, steam and gas turbines, diesel engines;
- build, operate and maintain control systems;
- operate and maintain heat pump systems with weather-dependent and remote heating control;
- operate wind turbines and even develop their own design (or improve the existing one);
- design, test and maintain power distribution networks;
- operate and maintain the intellectual steamshop remote control;
- develop alternative energy resources;
- test the equipment using the thermal network hydraulic stand.
Project-Based Learning (PBL)
PBL means either the real-world problem to be solved, or the industrial partner task to be accomplished. SUSU energy students and staff are involved in both: product development projects, which you might possibly turn into business later, and energy solutions we develop to meet the needs of either industry or municipal authorities. We are currently running several projects funded by either industrial companies or international funds or by city authorities. Some of them are optimization of efficiency of giant wind turbines, development of energy-efficient heat power stations, designing digital twins for electric drives, designing sustainable infrastructure of smart city.